Kalyan K. Sen - Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Kalyan K. Sen - Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid using SMART Power Flow Controllers
Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid using SMART Power Flow Controllers
Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
3 Chapter 3Figure 3‐1 EMTP modeling structure.Figure 3‐2 Single‐line diagram of a three‐phase voltage source with a source...Figure 3‐3 The A ‐phase voltage ( v 1Apu).Figure 3‐4 Single‐line diagram of a two‐generator/single‐line power system n...Figure 3‐5 Single‐line diagram of a two‐generator/single‐line power system w...Figure 3‐6 A ‐phase line voltage ( v 1A) at the BUS01 node, its peak value ( V 1)...Figure 3‐7 Block diagram of a Vector PLL.Figure 3‐8 A ‐phase line voltage ( v 1A) at BUS01 node, its peak value ( V 1), an...Figure 3‐9 Block diagram of a steady‐state resistance calculator.Figure 3‐10 Mathematical models of the (a) ST and (b) UPFC. Note the differe...Figure 3‐11 Variations of exchanged powers between the transmission line and...Figure 3‐12 Variations of node voltage with the operation of the ST and UPFC...Figure 3‐13 Variations of the receiving‐end power flows with the operations ...Figure 3‐14 Comparison of the active and reactive power flows at the receivi...
4 Chapter 4Figure 4‐1 (a) Autotransformer. (b) two‐winding transformer.Figure 4‐2 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending an...Figure 4‐3 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending an...Figure 4‐4 (a) Voltage‐regulating transformer (shunt‐series configuration); ...Figure 4‐5 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending an...Figure 4‐6 (a) Voltage‐regulating transformer (two‐winding transformer); (b)...Figure 4‐7 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending an...Figure 4‐8 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending an...Figure 4‐9 (a) PAR (asym) configuration in a bypass‐mode of operation; (b) p...Figure 4‐10 (a) PAR (asym) configuration for decreasing power flow; (b) phas...Figure 4‐11 (a) PAR (asym) configuration for increasing power flow; (b) phas...Figure 4‐12 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending a...Figure 4‐13 (a) PAR (sym) configuration in a bypass‐mode of operation; (b) p...Figure 4‐14 (a) PAR (sym) configuration for decreasing power flow; (b) phaso...Figure 4‐15 (a) PAR (sym) configuration for increasing power flow; (b) phaso...Figure 4‐16 Ranges of voltage magnitudes ( V sand V s′) at the sending a...
5 Chapter 5Figure 5‐1 Shunt‐compensating, mechanically‐switched capacitor, connected to...Figure 5‐2 Exchanged reactive power ( Q sh), the resulting voltages ( v 1Aand V Figure 5‐3 Shunt‐compensating, mechanically‐switched capacitor with a series...Figure 5‐4 Exchanged reactive power ( Q sh), the resulting voltages ( v 1Aand V Figure 5‐5 Shunt‐compensating, mechanically‐switched reactor, connected to a...Figure 5‐6 Exchanged reactive power ( Q sh), the resulting voltages ( v 1Aand V Figure 5‐7 Series‐compensating, mechanically‐switched reactors, connected in...Figure 5‐8 Exchanged reactive power ( Q se), the resulting voltage ( v 12A), cur...Figure 5‐9 Instantaneous filtered magnitude of the voltage across the series...Figure 5‐10 Instantaneous filtered phase angle of the voltage across the ser...Figure 5‐11 Instantaneous magnitude ( i dq) of the current through the series‐...Figure 5‐12 Instantaneous phase angle ( θ idq) of the current through the...Figure 5‐13 Instantaneous magnitude ( z se) of the impedance of the series‐com...Figure 5‐14 Instantaneous phase angle ( θ zse) of the voltage across the ...Figure 5‐15 Instantaneous relative phase angle ( β ) of the series‐compen...Figure 5‐16 Two superimposed voltages: (1) A phase of the calculated compens...Figure 5‐17 Series‐compensating, mechanically‐switched capacitor with a reac...Figure 5‐18 Exchanged reactive power ( Q se), the resulting voltage ( v 12A), cu...Figure 5‐19 Series‐compensating voltage to emulate a reactor in series with ...Figure 5‐20 Validation of a series‐compensating voltage as an emulated react...
6 Chapter 6Figure 6‐1 (a) Two‐generator/one‐line uncompensated power system network; (b...Figure 6‐2 (a) Two‐generator/one‐line power system network with a series‐com...Figure 6‐3 Transformer/LTCs‐based solutions for power flow controllers using...Figure 6‐4 (a) Voltage‐Regulating Transformer (Shunt‐Series configuration); ...Figure 6‐5 (a) Voltage‐Regulating Transformer (Shunt‐Shunt configuration); (...Figure 6‐6 (a) Phase Angle Regulator (asymmetric); (b) phasor diagram.Figure 6‐7 (a, b) Effect of a series‐compensating voltage on power flow in a...Figure 6‐8 (a) Voltage‐Regulating Transformer for increasing line voltage; (...Figure 6‐9 (a) Voltage‐Regulating Transformer for decreasing line voltage; (...Figure 6‐10 (a) ST for voltage regulation; (b) phasor diagram.Figure 6‐11 (a) ST for voltage compensation with 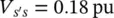 and β = 106.1°; (b) ...Figure 6‐12 Compensating points with the use of the ST within the entire ran...Figure 6‐13 Series impedance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐14 Series resistance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐15 Series reactance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐16 Closed‐loop automatic power flow control block diagram of the ST...Figure 6‐17 Open‐loop Compensating‐Voltage Unit control block diagram of the...Figure 6‐18 Selection of tap positions (Faruque and Dinavahi‐2007).Figure 6‐19 Compensating voltage ( V s′s) in pu during the entire range ...Figure 6‐20 Modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′) in pu during the entire...Figure 6‐21 Phase‐shift angle ( ψ ) in degrees during the entire range of...Figure 6‐22 (a) Active power ( P r), (b) reactive power ( Q r), and (c) apparent...Figure 6‐23 Active power ( P r) versus reactive power ( Q r) in pu at the receiv...Figure 6‐24 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se), (b) reactive power ( Q se), and ...Figure 6‐25 Exchanged active power ( P se ) versus reactive power ( Q se) in pu...Figure 6‐26 Line current ( I ) in pu during the entire range of the relative p...Figure 6‐27 (a) Sen Transformer (ST) and (b) phasor diagram.Figure 6‐28 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐29 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐30 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐31 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐32 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar at th...Figure 6‐33 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐34 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐35 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relative...Figure 6‐36 Three‐generator/four‐line power system network, integrated with ...Figure 6‐37 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐38 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐39 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐40 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐41 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar at th...Figure 6‐42 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐43 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐44 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relative...Figure 6‐45 Factory test circuit of an ST.Figure 6‐46 The instantaneous A ‐phase, sending‐end current ( i sA), line curre...Figure 6‐47 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐48 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐49 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐50 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐51 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar flows...Figure 6‐52 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐53 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐54 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relati...Figure 6‐55 Modified factory test circuit of an ST.Figure 6‐56 The instantaneous A ‐phase, sending‐end current ( i sA), line curre...Figure 6‐57 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) during the e...Figure 6‐58 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) dur...Figure 6‐59 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐60 (a) Active power ( P r), (b) reactive power ( Q r), and (c) apparent...Figure 6‐61 Active power ( P r) versus reactive power ( Q r) flows at the receiv...Figure 6‐62 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se), (b) reactive power ( Q se), and ...Figure 6‐63 Exchanged active power ( P se) versus reactive power ( Q se) by the ...Figure 6‐64 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relati...Figure 6‐65 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐66 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐67 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐68 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐69 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐70 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐71 (a) ST configuration using LTCs with lower current rating; (b) p...Figure 6‐72 ST configuration using taps with lower voltage and current ratin...Figure 6‐73 ST configuration with six secondary windings in a two‐core desig...Figure 6‐74 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 1 conf...Figure 6‐75 ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core des...Figure 6‐76 Operating points of an ST in Option 1: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐77 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 2 conf...Figure 6‐78 ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core des...Figure 6‐79 Operating points of an ST in Option 2: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐80 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 3 conf...Figure 6‐81 An ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core ...Figure 6‐82 Operating points of an ST in Option 3: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐83 (a) UPFC test results for automatic power flow control mode of o...Figure 6‐84 Practical voltage compensation range with the use of the VRT, PA...Figure 6‐85 Multiline Sen Transformer (MST).Figure 6‐86 ST’s Compensating‐Voltage Unit is connected to the stepped‐down ...Figure 6‐87 ST’s Compensating‐Voltage Unit is connected to the stepped‐up vo...Figure 6‐88 Two methods of modifying a transmission line voltage: (a) with a...Figure 6‐89 (a) Shunt‐Shunt configuration of ST for the A phase; (b) phasor ...Figure 6‐90 Shunt‐Shunt configuration of ST for the A phase, B phase, and C ...Figure 6‐91 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐92 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐93 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐94 MST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Units.Figure 6‐95 Generalized Sen Transformer (GST).
and β = 106.1°; (b) ...Figure 6‐12 Compensating points with the use of the ST within the entire ran...Figure 6‐13 Series impedance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐14 Series resistance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐15 Series reactance emulation control block diagram of the ST.Figure 6‐16 Closed‐loop automatic power flow control block diagram of the ST...Figure 6‐17 Open‐loop Compensating‐Voltage Unit control block diagram of the...Figure 6‐18 Selection of tap positions (Faruque and Dinavahi‐2007).Figure 6‐19 Compensating voltage ( V s′s) in pu during the entire range ...Figure 6‐20 Modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′) in pu during the entire...Figure 6‐21 Phase‐shift angle ( ψ ) in degrees during the entire range of...Figure 6‐22 (a) Active power ( P r), (b) reactive power ( Q r), and (c) apparent...Figure 6‐23 Active power ( P r) versus reactive power ( Q r) in pu at the receiv...Figure 6‐24 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se), (b) reactive power ( Q se), and ...Figure 6‐25 Exchanged active power ( P se ) versus reactive power ( Q se) in pu...Figure 6‐26 Line current ( I ) in pu during the entire range of the relative p...Figure 6‐27 (a) Sen Transformer (ST) and (b) phasor diagram.Figure 6‐28 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐29 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐30 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐31 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐32 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar at th...Figure 6‐33 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐34 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐35 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relative...Figure 6‐36 Three‐generator/four‐line power system network, integrated with ...Figure 6‐37 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐38 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐39 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐40 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐41 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar at th...Figure 6‐42 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐43 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐44 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relative...Figure 6‐45 Factory test circuit of an ST.Figure 6‐46 The instantaneous A ‐phase, sending‐end current ( i sA), line curre...Figure 6‐47 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) in pu during...Figure 6‐48 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) in ...Figure 6‐49 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐50 (a) Active power ( P r) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar, an...Figure 6‐51 Active power ( P r) in MW versus reactive power ( Q r) in Mvar flows...Figure 6‐52 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW, (b) reactive power ( Q se)...Figure 6‐53 Exchanged active power ( P se) in MW versus reactive power ( Q se) i...Figure 6‐54 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relati...Figure 6‐55 Modified factory test circuit of an ST.Figure 6‐56 The instantaneous A ‐phase, sending‐end current ( i sA), line curre...Figure 6‐57 Magnitude of the simulated sending‐end voltage ( V s) during the e...Figure 6‐58 Magnitude of the simulated compensating voltage ( V s′s) dur...Figure 6‐59 Magnitude of the simulated modified sending‐end voltage ( V s′...Figure 6‐60 (a) Active power ( P r), (b) reactive power ( Q r), and (c) apparent...Figure 6‐61 Active power ( P r) versus reactive power ( Q r) flows at the receiv...Figure 6‐62 (a) Exchanged active power ( P se), (b) reactive power ( Q se), and ...Figure 6‐63 Exchanged active power ( P se) versus reactive power ( Q se) by the ...Figure 6‐64 Line current ( I ) in A rmsduring the entire range of the relati...Figure 6‐65 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐66 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐67 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐68 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐69 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐70 (a) ST operating with a compensating voltage in the range of 0 ≤...Figure 6‐71 (a) ST configuration using LTCs with lower current rating; (b) p...Figure 6‐72 ST configuration using taps with lower voltage and current ratin...Figure 6‐73 ST configuration with six secondary windings in a two‐core desig...Figure 6‐74 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 1 conf...Figure 6‐75 ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core des...Figure 6‐76 Operating points of an ST in Option 1: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐77 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 2 conf...Figure 6‐78 ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core des...Figure 6‐79 Operating points of an ST in Option 2: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐80 The voltage compensating points for the A phase in Option 3 conf...Figure 6‐81 An ST configuration with three secondary windings in a two‐core ...Figure 6‐82 Operating points of an ST in Option 3: (a) modified sending‐end ...Figure 6‐83 (a) UPFC test results for automatic power flow control mode of o...Figure 6‐84 Practical voltage compensation range with the use of the VRT, PA...Figure 6‐85 Multiline Sen Transformer (MST).Figure 6‐86 ST’s Compensating‐Voltage Unit is connected to the stepped‐down ...Figure 6‐87 ST’s Compensating‐Voltage Unit is connected to the stepped‐up vo...Figure 6‐88 Two methods of modifying a transmission line voltage: (a) with a...Figure 6‐89 (a) Shunt‐Shunt configuration of ST for the A phase; (b) phasor ...Figure 6‐90 Shunt‐Shunt configuration of ST for the A phase, B phase, and C ...Figure 6‐91 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐92 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐93 (a) ST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Unit operating ...Figure 6‐94 MST with shunt‐connected Compensating‐Voltage Units.Figure 6‐95 Generalized Sen Transformer (GST).
Интервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Power Flow Control Solutions for a Modern Grid Using SMART Power Flow Controllers» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












