Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
The most comprehensive and up-to-date study of smart charging solutions for hybrid and electric vehicles for engineers, scientists, students, and other professionals. Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles:
Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
The previous sections and subsections have described the requirements of intelligent systems for the deployment of smart charging architectures. The development of intelligent systems demands data. The data in the electricity grid is generally saved in separate database servers which are used for future planning and expansion of the operation [57, 69, 70]. Hence, designing an intelligent system using AI at the electricity grid side can be attempted, but, when a developer looks to develop intelligent systems for the consumers, lack of data is a big challenge. Hence, the digitalization of the complete smart charging infrastructure can be an initial step to plan for smart charging [67].
Digitalization with an assurance of data analytics can help in developing business models, components, software, and connected hardware and an understanding of the expectations of the consumers. The data logged, when analyzed, can reveal various day and night charging patterns, user preferences, the requirement of power to charge, and various ancillary services that can be attached to EVs [71]. Further, the deployment of communication architecture requires decisions to be made on the communication channel to be used. The data analyzed can also help to provide useful insights to decide the data rate. Based on the data rate, communication channels can be selected. Thus, data analytics and AI are important enablers of the smart charging system.
Apart from technologies that add intelligence, billing and payment services are also an essential part of smart charging systems. Advancements in technologies such as blockchain, which provides secured transactions and maintains a ledger, are being utilized. Blockchains have distributed architectures and the operation is based on secured databases that maintain a record of all transactions. The transactions are verified by the users’ computational or connecting devices (computer, mobile phone, or any smart devices) called nodes. The technology is preferred to be used in smart charging systems due to security and distributed architecture.
Thus, blockchain technology has also emerged as an enabler in smart charging systems [67, 69].
1.7 Control Architectures
Communication channels interconnect the components in a smart charging system, but the interconnection does not result in a successful operation. The operation requires controllers which either command centrally or are distributed in the subsystems to make decisions. The next subsections will describe different architectures in which the controller is deployed in smart charging systems for smooth monitoring and operation [10, 13, 15, 27, 31, 33, 43].
1.7.1 Centralized
The centralized control system for smart charging systems demands robust communication infrastructure. In a centralized control, necessary data is transmitted from each connected entity to the central controller. The controller performs decision making by determining the optimal solution considering constraints of both the EV user and the utility grid. The solution can be related to the direction of power flow, electricity cost, allowable charging rate, scheduling of charging and discharging of EVs, and power management. The central control, in a few cases, is supported by the necessary algorithms that process the data. The processing of data includes error check, relevant parameter estimations, data storage, and analysis. Nonetheless, the centralized control system determines solutions or makes decisions considering information from the entire system [9, 10]. A schematic of the centralized controller is shown in Figure 1.5. Each of the entities shown connected by dotted lines depicts communication links.
The major drawback of the central controller in a smart charging system is an optimization problem. The optimization problem becomes very large and complex as it involves numerous parameters from different entities. The controller’s failure in the centralized control system will result in a complete halt in operation or incur huge losses to the connected components. Further, scalability is another challenge when the optimization problem exceeds the constraints, such as the maximum number of EVs or charging stations [72-74]. The drawbacks of the centralized controller are outfitted by adopting hierarchical control architecture. Several controllers are deployed to administer a particular function. In contrast, the central controller is given the responsibility to monitor and perform load demand response. The hierarchical architecture resulted in reduced computational requirements [75, 76]. However, the risk of a negative impact on the smart charging system due to centralized control is not largely reduced.

Figure 1.5 Schematic of centralized controller in smart charging architecture.
1.7.2 Decentralized
Decentralized control, contrary to centralized, has distributed control and optimization modules. Charging of EVs takes place spatially in a distributed manner. Hence, the planning of decentralized control in smart charging systems is considered to be safe and reliable. In decentralized control, decision making takes place locally, where the EV charging takes place. The requirement of extensive and reliable communication systems, large and complete optimization, and the risk of damage due to a controller’s incorrect decision is readily reduced [74, 77]. The only challenge is performing load management. The data exchange between the utility grid and EV users still demands communication systems. The schematic of decentralized control is shown in Figure 1.6. Each entity has a local level controller and aggregator that are connected to a central controller. The distribution of tasks assigned to each local controller reduces the burden of the central controller to a large extent as compared to the centralized controller scheme.
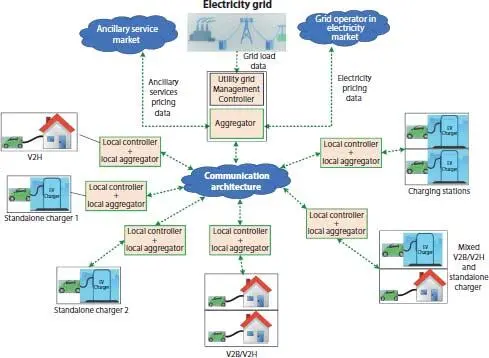
Figure 1.6 Schematic of decentralized controller in smart charging architecture.
The simplicity in the implementation of the decentralized controller is leading to an increase in demand. Further, the coherency, like EV operation (spatially distributed), reduces deployment complexity. Further, decentralized control architectures are seemingly practical and scalable, considering their computational complexity [78].
Table 1.3briefly presents the difference between the control architectures: centralized and decentralized. Based on the merits and demerits, the required architecture can be selected for the design of smart charging systems.
1.7.3 Comments on Suitability
The drawbacks and benefits of centralized and decentralized control architecture infer a requirement for maturity in the smart charging system.
Table 1.3 List of Differences between control architectures in a smart charging system.
| Control architecture | Merits | Demerits |
|---|---|---|
| Centralized | Better voltage and frequency regulationBetter utilization of network capacityCan be used with provisions for ancillary servicesEase of control and operation inclined towards the PSO | System design and deployment are complexDemands huge capital investment in developing robust communication architectureDifficult to scale due to predefined constraints in the optimization problemHigh computational requirements to process and analyze a large amount of dataRobust error correction of data protection is required |
| Decentralized | Ease in the tracking of fault in the systemMore control to the EV users and higher acceptance rateLess capital investment in deploying communication architectureEasily scalableEase of renewable energy integration | The impact on the utility grid is tough to determineThe use of EVs as ancillary services is difficult to implement |
During the initial push for smart charging systems for EVs, decentralized architecture looks more acceptable and easier to implement. Further, the demography and topography of the area also significantly impact the selection of control architecture. For an area with higher demography, the decentralized control architecture will resemble centralized control.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Smart Charging Solutions for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












