David V. Tennant - Product Development
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «David V. Tennant - Product Development» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Product Development
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Product Development: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Product Development»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
An insightful development roadmap to help engineers and businesspeople successfully bring a product to market Product Development: An Engineer’s Guide to Business Considerations, Real-World Product Testing, and Launch,
Product Development
Product Development
Product Development — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Product Development», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
What Is Product Development?
We first need to ask ourselves, what is a product? A product is simply an item or service that brings value to the customer in exchange for a price. You may find it odd that a “service” can be considered a product, but it is. A service can be a utility providing electricity to its customers. It can be an insurance policy that you purchase for your car, or the lawn service that keeps your company’s green spaces looking nice. Services can also be developed and sold similar to “hard” products. While services can be considered a product, marketing services is different from marketing a hard product. Further, think about apps that are developed for your smartphone. Are these a product or a service? Sometimes the line can be blurry.
It is appropriate to consider that products can originate from a variety of sources. Perhaps your R&D group has developed a new smart widget. It is most likely now the engineering department’s mission to determine how to commercialize it and manufacture it in a cost-effective manner.
The marketing group will need to determine the channels necessary to distribute the widget, how to develop a sales and marketing strategy, and determine estimates for pricing, profit, breakeven point, etc. Essentially, there are many moving parts to successfully launching a product. Where do products come from? Figure 1.2 shows some (but not all) of the points whereby ideas for new products are generated.
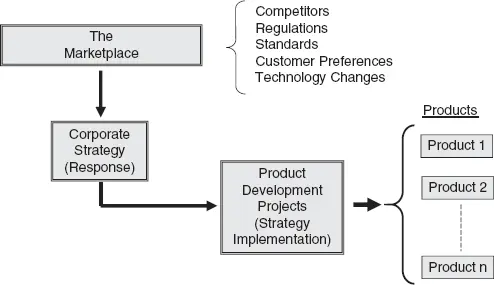
Figure 1.2 Types of optimization models.
How This Book Is Organized
It is suggested the reader go through each chapter in sequence. This is because each chapter builds on concepts presented in the previous chapters. Also, developing products should have a structured approach and this book provides this in the correct order.
In many chapters, there are “Tabletop Discussion” questions. These are provided for group discussions and should have about a 30-minute time frame. These should encourage students or product teams thinking about key topics and how to address them.
Case studies are included to reinforce the concepts presented in each chapter. While there are one or two “hypothetical” cases, most of the cases presented are real-world examples. The author has had significant experience in rescuing projects (or product developments) that were in deep trouble. In these instances, it would be in poor taste to name companies or individuals. Many of these cases challenge the reader with questions pertaining to how they would have addressed, prevented, or rescued these difficult issues.
Key points are summarized at the end of each chapter, followed by questions for students or readers to answer.
The answers to both the case studies and questions are also provided.
Subsequent chapters include:
Chapter 2– The Role of Marketing
This provides an overall perspective on the basics of marketing, how it is different from sales, and how pricing, product, promotion, and place are part of a strategy. Marketing many times drives new products; indeed, a marketing professional may be placed in charge of a product’s development. Marketing also performs competitor analysis, obtains customer feedback (e.g., focus groups), and develops sophisticated models – usually an Excel spreadsheet – to evaluate pricing sensitivity.
Chapter 3– The Role of Engineering
Engineers play a key role in the development of products. And there are many disciplines in this field. Listed in Chapter 3are the types of engineering – mechanical, electrical, instrumentation, etc. – and how they work together to develop a project. There is a controlled approach to defining and solving engineering problems. Also, computer modeling can reduce development time and reduce the number of prototypes that are produced.
In addition to the technical challenges, engineers often have to design a product with the potential to be misused, either accidentally or intentionally. This brings into focus the need to consider ergonomics (human factors engineering) and product liability issues.
Chapter 4– Core Team and Teamwork
Which groups and who should be involved in the product’s development? What is the role of executive management in the process? These questions are evaluated from the perspective that a team is required. How do teams work together to be most effective? The use of matrixed teams – so common in many large companies – can be positive or detrimental depending on the organization. Teamwork and leadership relative to product development will be explored.
This chapter will also look at the role of the accounting, finance, and supply chain (procurement) departments. Having a product that continuously goes over budget will affect its profitability and have the potential for product cancellation, if left unchecked. This chapter is important as it clearly defines the roles of these functional areas and their contribution to a product’s development.
Chapter 5– Getting Started
Once a product/project has been approved by senior management, how do we get started? The reader will learn how the business case, typically a marketing function or feasibility study, is the springboard to developing an action plan. Also, the differences between basic and applied research will be presented. How does R&D (research and development) participate in a product’s development?
The concepts of formal project management (and several case studies) will be offered along with the top reasons that projects, or product developments, fail. Both agile and traditional project management theories will be presented and understanding when to use them.
Chapter 6– Product Development for Small Firms and Entrepreneurs
Small firms have a set of challenges that are unique. Many times, obtaining credit, business loans, or investors is a challenge. This is not something a larger, well-established firm is concerned with. However, this chapter delves into sources of funding (venture capital, angel investors, etc.) and where to find local incubators, which are set up to assist small companies and inventors with skills, training, and business contacts.
Many times, small firms or inventors do not have access to talent such as engineering or manufacturing companies. These are discussed along with product roadmaps and when or if to obtain a patent.
Chapter 7– Manufacturing the New Product
A history of Japan’s focus on quality and manufacturing is explored along with a history of America’s car companies from the 1960s. Technology, government policies, foreign competition, and other factors can impact design and manufacturing. Just-in-time and lean manufacturing are presented with the benefits and drawbacks to each.
A review of small vs. large manufacturers and domestic vs. offshore will be offered. Further, an overview of current manufacturing techniques will be offered as well as a discussion on what manufacturing will look like in the future: 5 G, artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and robotics.
Chapter 8– Engineering Product Design and Testing
The project lifecycle is introduced along with methods to perform risk reviews. A risk is simply a potential, future problem that can ruin your project. A risk review can assist in identifying problems and developing mitigation strategies.
A discussion and an example of engineering modeling is presented. This illustrates how modeling saves time and can be very reliable. Supply chain is equally important as it must work closely with engineering in issuing RFPs and technical specifications. The chapter closes with a review of new technologies and the importance of identifying stakeholders.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Product Development»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Product Development» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Product Development» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.











