Among Asian-Pacific regulators, the Australian Prudential Regulation Authority (APRA) refers to non-financial risks in its information paper on governance, culture, remuneration and accountability. However, it does not provide an explicit definition of non-financial risk. [28]
2.3 Differentiation of financial and non-financial risk
Given the lack of clarity concerning a standardised definition of non-financial risk, we here define the terms ‘financial risk’ and ‘non-financial risk’ the way we will use them throughout this book. The general approach considers regulatory definitions already in use and attempts to find a structure that encompasses all types of risk.
Financial risk can generally be defined as “the possibility of losing money on an investment or business venture.” [29]Other categorisations of financial risk use the question of measurability, meaning whether methodologies are available to accurately model and measure risk.
However, as both approaches do not clearly define the risk types that would be considered under financial risk, our definition of financial risk is based on a positive-list approach, defining all risk types that belong in this risk category. Non-financial risk is then defined as the remaining risk types. Moreover, due to the importance of the term “operational risk,” which is a supercategory for certain, yet not all non-financial risks, non-financial risk itself is subdivided into two key categories: operational risks and strategic risks. Taken together, this approach covers all types of risks possible in financial institutions.
2.3.1 Financial risk definition
Our definition of financial risk is based on the enumeration of all included individual financial risk types. For the purposes of this book, the three financial risk types included in the definition of financial risk are credit risk, market risk and liquidity risk.
The BCBS defines credit risk as “the potential that a bank borrower or counterparty will fail to meet its obligations in accordance with agreed terms.” [30]For the purpose of risk quantification and the calculation of capital requirements, credit risk is separated into three main risk parameters. Those used to measure credit risk are probability of default (PD), loss given default (LGD) and the exposure at default (EAD). When all these parameters are estimated, their product equals the expected loss (EL), which can either be viewed on an individual loan, a customer or a portfolio level. However, the expected loss as such does not pose credit risk to a bank, as it is required to hold risk provisions for expected losses. The actual credit risk here is the risk of unexpected losses, or the deviation from the expected loss. This risk needs to be covered by banks by holding sufficient capital against potential unexpected losses, as specified by regulatory capital requirements.
Market risk, according to the BCBS, is defined as “the risk of losses in on and off-balance-sheet positions arising from movements in market prices.” [31]In contrast to credit risk, which is a pure downside risk, market price movements also include the possibility of gains instead of losses.
Liquidity risk as defined by the BCBS contains two components: funding liquidity risk and market liquidity risk.
“Funding liquidity risk is the risk that the firm will not be able to meet efficiently both expected and unexpected current and future cash flow and collateral needs without affecting either daily operations or the financial condition of the firm. Market liquidity risk is the risk that a firm cannot easily offset or eliminate a position at the market price because of inadequate market depth or market disruption.” [32]
2.3.2 Non-financial risk definition
The definition of non-financial risk is not as straightforward as for financial risk. In contrast to the positive definition of financial risk as being comprised of certain risk types, non-financial risks for the purposes of this book are defined as comprising all risk types that are not included in the definition of financial risk .
As pointed out previously, there is no clear catalogue or definition of non-financial risks. In addition, definitions of risk types overlap partially and cannot be as clearly established as financial risks.
The risk types under non-financial risk can, in turn, be structured into two key categories. The first category contains operational risks, which are those relating to banking operations. The other category contains those risks that we view as strategic risks, which makes them part of non-financial risks but sets them apart from risks related to operations. This approach combines the specification of operational risks according to the BCBS definition, including the fact that strategic risks are also non-financial risks.
2.4 Specific clusters of non-financial risk
This section takes a closer look at the different clusters of risk types that comprise all versions of non-financial risk according to the general definition in section 3.2.
Figure 2:Risk taxonomy in financial institutions
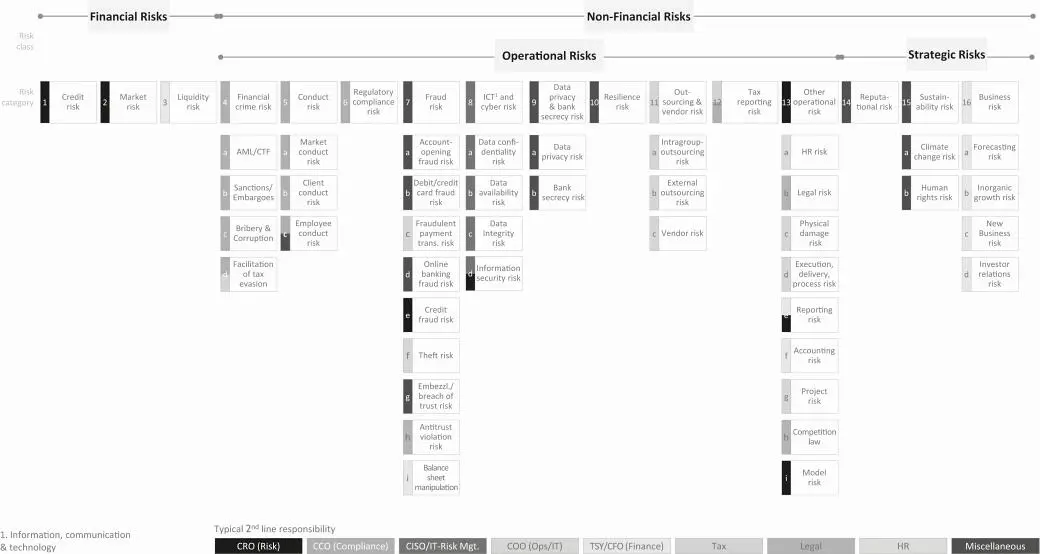
Non-financial risk contains the following risk types:
Operational risk:
Financial crime risk
Conduct risk
Regulatory compliance risk
Fraud risk
Information, communication & technology (ICT) and cyber risk
Data privacy and bank secrecy risk
Resilience risk
Outsourcing & vendor risk
Tax reporting risk
Other operational risk
Strategic risk:
Reputational risk
Sustainability risk
Business risk
In the following section, we will provide definitions of the individual types of non-financial risks. If available, we provide an overview and comparison of definitions of the risk types as used by the different regulatory bodies or global associations.
We focus on the BCBS for global definitions. Concerning European regulators, we mainly cover the EBA, European Central Bank, the UK Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA) and the UK Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). Concerning North American regulators, we focus on the FED, the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) and the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). Concerning Asian-Pacific regulators, we mainly cover the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS), the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) and the APRA.
Operational risk as a risk type has been in use by regulators since Basel II. [33]This risk type – along with the financial risk types of credit risk and market risk – is still the basis for the capital requirements calculation of the Basel framework’s first pillar. According to the BCBS, operational risk is defined as “the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. This definition includes legal risk but excludes strategic and reputational risk.” [34]
In Europe, the PRA makes use of the Basel definition. For the special case of funds, the FCA uses one further specification by stating that it includes “legal and documentation risk and the risk resulting from the trading, settlement and valuation procedures operated on behalf of the fund.” [35]The EBA and the Central Bank of Ireland use definitions in line with the Basel definition.
Both in the US (Federal Reserve Bank of New York and FDIC) and in Canada (OSFI), the regulators use the Basel definition. In Asia-Pacific, the APRA also uses the Basel definition. Therefore, for the purpose of this book, we use the Basel definition of operational risk.
Читать дальше













