Avy Joseph - Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Avy Joseph - Cognitive Behaviour Therapy» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: unrecognised, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Cognitive Behaviour Therapy»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy
Cognitive Behaviour Therapy — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Cognitive Behaviour Therapy», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
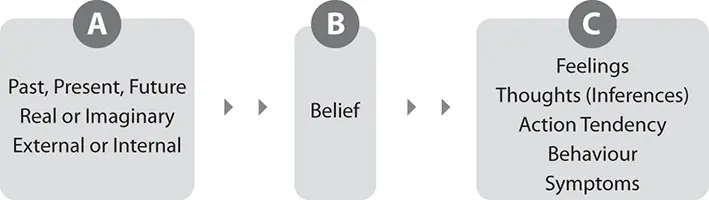
Beliefs
According to the ABC model we can have two types of beliefs – rational and irrational or healthy and unhealthy.
1 Healthy beliefs:Are flexibleAre based on the things that you want, like, desire and preferTend to make sense – they are logical and consistent with realityMeans accepting that sometimes you may not get what you wantDetach human worth from success or failureLead to emotional well‐being and set you up for goal achievement.
2 Unhealthy beliefs:Are unrealisticCan be self‐criticalAre not based on acceptance or acknowledgement of realityDo not acknowledge or accept other possibilities (even though reality shows that other possibilities exist)Cause a mismatch between internal and external realitiesLead to emotional disturbance and set you up for failure and goal sabotage.
Compare the following statements:
‘I would like it to be nice and sunny every day when I wake up but I accept there is a chance that it might not be.’
‘The day MUST be nice and sunny when I wake up’
The second example is unhealthy and irrational because it is unrealistic. Unhealthy beliefs do not make logical sense. What makes sense is to have a more healthy belief, such as ‘I would like the day to be nice and sunny when I wake up, but it doesn't mean that it HAS to be.’
Healthy negative emotions and self‐helping behaviours
It is easy to understand that if you hold a healthy belief about yourself or about certain things in your life, this would increase your chances of success. However, success is never guaranteed, so if you don't succeed you might feel upset and sad. Having healthy beliefs means that, while you might feel sad or upset if you failed you would lick your wounds, dust yourself off and focus back on your goal. Instead of feeling guilty you might feel regret and look at ways of improving. Instead of feeling unhealthy anger or rage, you might feel annoyed. You would behave assertively without lashing out in a destructive way or giving up. You would believe that you are not a failure as a human being but rather that you are a fallible human being who is able to learn and improve.
Unhealthy negative emotions and self‐destructive behaviours
It is not difficult to understand that if you have unhealthy beliefs about yourself and about certain things in your life, your feelings and behaviours are not going to be healthy.
According to the ABC model, unhealthy beliefs provoke unhealthy negative emotions and self‐damaging or destructive behaviours. Depression, anxiety, guilt and rage are examples of unhealthy negative emotions.
ANXIETY VERSUS CONCERN
| Unhealthy Negative Emotion | What the belief is about | Healthy Negative Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety | A threat or danger | Concern |
| How you think | How you think | |
| You exaggerate the overall effect of the threat. | You keep the effect of the danger in perspective. | |
| You think that you won't be able to deal with the danger. | You have a balanced view about your ability to deal with the threat. | |
| You see the glass as half empty. | You see the whole glass and focus on the full part. | |
| Your thoughts are not constructive. | Your thoughts are solution‐focused and constructive. | |
| What you do or what you feel like doing | What you do or what you feel like doing | |
| Run away physically. | Face the threat. | |
| Run away mentally. | Deal with the potential danger. | |
| Do superstitious things to get rid of the threat. | ||
| Medicate and numb your feelings, e.g. with alcohol. | ||
| Seek assurances from others. |
DEPRESSION VERSUS SADNESS
| Unhealthy Negative Emotion | What the belief is about | Healthy Negative Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | Loss or failure | Sadness |
| How you think | How you think | |
| You only focus on negatives since the loss or failure. | You think of both the negatives and positives of the loss or failure. | |
| You think of all the other past losses and failures. | You do not dwell on past losses and failures. | |
| You think you are a failure, helpless. | You do not see yourself as a failure or as helpless. You think that you can help yourself to move forward. | |
| You think the future is hopeless, bleak and full of misery. | You have hope for the future. | |
| What you do or what you feel like doing | What you do or what you feel like doing | |
| You pull away from other people. | You express how you feel about your loss or failure. | |
| You withdraw into your head. | You look after yourself and your environment. | |
| You stop looking after yourself and your environment. | You engage in healthy behaviours. | |
| You get rid of your emotions in destructive ways, e.g. alcohol or overeating. |
ANGER/RAGE VERSUS ANNOYANCE
| Unhealthy Negative Emotion | What the belief is about | Healthy Negative Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Anger or rage | Loss or failure | Sadness |
| How you think | How you think | |
| You exaggerate the actions of the person who has broken your personal rule. | You are balanced about the intention behind the thing that was done. | |
| You think the other person's intentions were malicious. | You don't see malice. | |
| You are right and the other person is definitely wrong. | You are open to being wrong. | |
| You can't see the other person's point of view. | You can listen to the other person's point of view. | |
| You think of how you can get your revenge. | You do not think of seeking revenge. | |
| What you do or what you feel like doing | What you do or what you feel like doing | |
| You physically attack. | You talk and behave in an assertive manner but with the right intent. | |
| You verbally attack. | You ask the other person to make changes but you don't demand it. | |
| You pay them back somehow, e.g. by ignoring them or staying silent. You recruit allies against the other person. |
HURT VERSUS SORROW
| Unhealthy Negative Emotion | What the belief is about | Healthy Negative Emotion |
|---|---|---|
| Hurt | Someone has treated you badly. You think you deserve to be treated better. | Sorrow |
| How you think | How you think | |
| You exaggerate the unfairness of your treatment. | You think in a balanced way about the unfairness. | |
| You think the other person does not care about you. | You do not think the other person does not care about you. | |
| You think of yourself as unlovable or misunderstood. | You do not think of yourself as unlovable or misunderstood. | |
| You remember the other times when you felt hurt. | You don't think about the other times when you felt hurt. | |
| The other person must understand and make amends first. | You don't insist the other person has to make the first move. | |
| What you do or what you feel like doing | What you do or what you feel like doing | |
| You sulk and shut down. | You talk about how you feel in order to persuade the other person to behave more fairly. | |
| You pick on the other person without telling them why. | ||
GUILT VERSUS REMORSE
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Cognitive Behaviour Therapy»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Cognitive Behaviour Therapy» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Cognitive Behaviour Therapy» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












