Alfred Wallace - Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Alfred Wallace - Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_edu, Биология, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Range of East Asian and North African Mammals. —Let us now pass to the other side of the great northern continent, and examine the list of the quadrupeds of Amoorland, in the same latitude as Germany. We find that there are forty-four terrestrial species (omitting the bats, the seals, and other marine animals), and of these no less than twenty-six are identical with European species, and twelve or thirteen more are closely allied representatives, leaving only five or six which are peculiarly Asiatic. We can hardly have a more convincing proof of the essential oneness of the mammalia of Europe and Northern Asia.
In Northern Africa we do not find so many European species (though even here they are very numerous) because a considerable number of West Asiatic and desert forms occur. Having, however, shown that Europe and Western Asia have almost identical animals, we may treat all these as really European, and we shall then be able to compare the quadrupeds of North Africa with those of Europe and West Asia. Taking those of Algeria as the best known, we find that there are thirty-three species identical with those of Europe and West Asia, while twenty-four more, though distinct, are closely allied, belonging to the same genera; thus making a total of fifty-seven of European type. On the other hand, we have seven species which are either identical with species of tropical Africa or allied to them, and six more which are especially characteristic of the African and Asiatic deserts which form a kind of neutral zone between the temperate and tropical regions. If now we consider that Algeria and the adjacent countries bordering the Mediterranean form part of Africa, while they are separated from Europe by a wide sea and are only connected with Asia by a narrow isthmus, we cannot but feel surprised at the wonderful preponderance of the European and West Asiatic elements in the mammalia which inhabit the district.
The Range of British Birds. —As it is very important that no doubt should exist as to the limits of the zoological region of which Europe forms a part, we will now examine the birds, in order to see how far they agree in their distribution with the mammalia. Of late years great attention has been paid to the distribution of European and Asiatic birds, many ornithologists having travelled in North Africa, in Palestine, in Asia Minor, in Persia, in Siberia, in Mongolia, and in China; so that we are now able to determine the exact ranges of many species in a manner that would have been impossible a few years ago. These ranges are given for all British species in the new edition of Yarrell's History of British Birds edited by Professor Newton, while those of all European birds are given in still more detail in Mr. Dresser's beautiful work on the birds of Europe. In order to confine our examination within reasonable limits, and at the same time give it the interest attaching to familiar objects, we will take the whole series of British Passeres or perching birds given in Professor Newton's work (118 in number) and arrange them in series according to the extent of their range. These include not only the permanent residents and regular migrants to our country, but also those which occasionally straggle here, so that it really comprises a large proportion of all European birds.
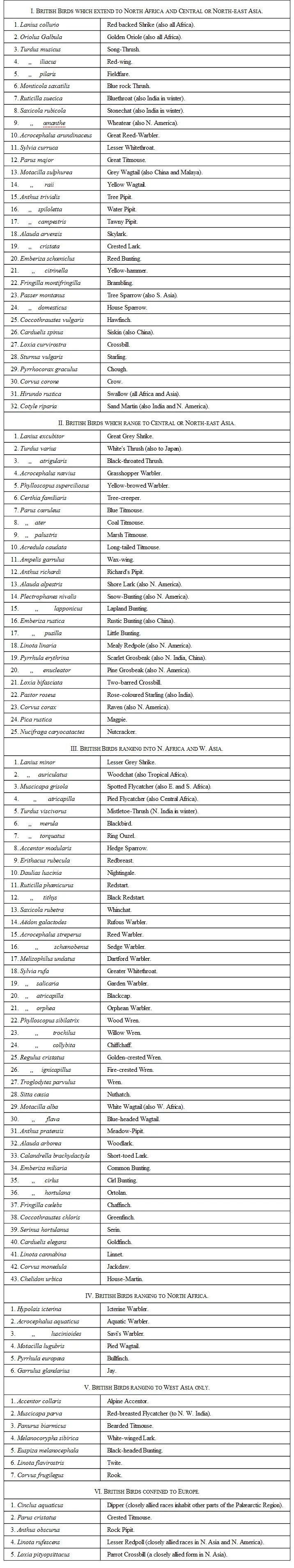
We find, that out of a total of 118 British Passeres there are:
32 species which range to North Africa and Central or East Asia.
25 species which range to Central or East Asia, but not to North Africa.
43 species which range to North Africa and Western Asia.
6 species which range to North Africa, but not at all into Asia.
7 species which range to West Asia, but not to North Africa.
5 species which do not range out of Europe.
These figures agree essentially with those furnished by the mammalia, and complete the demonstration that all the temperate portions of Asia and North Africa must be added to Europe to form a natural zoological division of the earth. We must also note how comparatively few of these overpass the limits thus indicated; only seven species extending their range occasionally into tropical or South Africa, eight into some parts of tropical Asia, and six into arctic or temperate North America.
Range of East Asian Birds. —To complete the evidence we only require to know that the East Asiatic birds are as much like those of Europe, as we have already shown to be the case when we take the point of departure from our end of the continent. This does not follow necessarily, because it is possible that a totally distinct North Asiatic fauna might there prevail; and, although our birds go eastward to the remotest parts of Asia, their birds might not come westward to Europe. The birds of Eastern Siberia have been carefully studied by Russian naturalists and afford us the means of making the required comparison. There are 151 species belonging to the orders Passeres and Picariæ (the perching and climbing birds), and of these no less than 77, or more than half, are absolutely identical with European species; 63 are peculiar to North Asia, but all except five or six of these are allied to European forms; the remaining 11 species are migrants from South-eastern Asia. The resemblance is therefore equally close whichever extremity of the Euro-Asiatic continent we take as our starting point, and is equally remarkable in birds as in mammalia. We have now only to determine the limits of this, our first zoological region, which has been termed the "Palæarctic" by Mr. Sclater, meaning the "northern old-world" region—a name now well known to naturalists.
The Limits of the Palæarctic Region. —The boundaries of this region, as nearly as they can be ascertained, are shown on our general map at the beginning of this chapter, but it will be evident on consideration, that, except in a few places, its limits can only be approximately defined. On the north, east, and west it extends to the ocean, and includes a number of islands whose peculiarities will be pointed out in a subsequent chapter; so that the southern boundary alone remains, but as this runs across the entire continent from the Atlantic to the Pacific ocean, often traversing little-known regions, we may perhaps never be able to determine it accurately, even if it admits of such determination. In drawing the boundary line across Africa we meet with our first difficulty. The Euro-Asiatic animals undoubtedly extend to the northern borders of the Sahara, while those of tropical Africa come up to its southern margin, the desert itself forming a kind of sandy ocean between them. Some of the species on either side penetrate and even cross the desert, but it is impossible to balance these with any accuracy, and it has therefore been thought best, as a mere matter of convenience, to consider the geographical line of the tropic of Cancer to form the boundary. We are thus enabled to define the Palæarctic region as including all north temperate Africa; and, a similar intermingling of animal types occurring in Arabia, the same boundary line is continued to the southern shore of the Persian Gulf. Persia and Afghanistan undoubtedly belong to the Palæarctic region, and Baluchistan should probably go with these. The boundary in the north-western part of India is again difficult to determine, but it cannot be far one way or the other from the river Indus as far up as Attock, opposite the mouth of the Cabool river. Here it will bend to the south-east, passing a little south of Cashmeer, and along the southern slopes of the Himalayas into East Thibet and China, at heights varying from 9,000 to 11,000 feet according to soil, aspect, and shelter. It may, perhaps, be defined as extending to the upper belt of forests as far as coniferous trees prevail; but the temperate and tropical faunas are here so intermingled that to draw any exact parting line is impossible. The two faunas are, however, very distinct. In and above the pine woods there are abundance of warblers of northern genera, with wrens, numerous titmice, and a great variety of buntings, grosbeaks, bullfinches and rosefinches, all more or less nearly allied to the birds of Europe and Northern Asia; while a little lower down we meet with a host of peculiar birds allied to those of tropical Asia and the Malay Islands, but often of distinct genera. There can be no doubt, therefore, of the existence here of a pretty sharp line of demarkation between the temperate and tropical faunas, though this line will be so irregular, owing to the complex system of valleys and ridges, that in our present ignorance of much of the country it cannot be marked in detail on any map.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Island Life; Or, The Phenomena and Causes of Insular Faunas and Floras» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












