Robert Armitage Sterndale - Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Robert Armitage Sterndale - Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon» — ознакомительный отрывок электронной книги совершенно бесплатно, а после прочтения отрывка купить полную версию. В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: foreign_edu, Биология, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon — читать онлайн ознакомительный отрывок
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
SIZE.—Head and body, 2-2/10 inches; tail, 1; wing expanse, 12.
Dr. Kellaart considered this a new and undescribed species, distinguished from H. speoris and H. vulgaris ( vel Templetonii —Kellaart) by the greater length of the fore-arm, which is two inches. This remark however does not apply to vulgaris , of which Kellaart himself gives two inches as the length of the radius, and Blyth gives two and a quarter. The absence of the frontal sac would have been a greater proof, but both specimens on which Kellaart made his observations were females; and as colouring is so varied in the bat tribe as to preclude the division of species on this ground, I think we may put this down as a doubtful species on which more information is desirable.
HABITAT.—India generally; Ceylon and Burmah.
DESCRIPTION.—The fur with three shades—buff, then reddish brown with ashy tips, underneath greyish or pale brown. "The hinder erect nose-leaf," according to Dobson's description, "equals the horse-shoe and slightly exceeds the sella in width, its free margin forming a segment of the circumference of a circle, with a small blunt projection in the centre and three vertical ridges on its concave front surface; sella large, with a prominent ridge in the centre, forming a small projection above and one smaller on each side; sides of the muzzle with prominent vertical leaves, three on each side; no frontal pore."
There is a good figure of the head of this bat in Cuvier's 'Animal Kingdom,' Carpenter's and Westwood's edition, under the name of Rhinolophus nobilis . It is the same also as Kellaart's Hipposideros lankadiva . Captain Hutton, who was a keen observer of the habits of the bats at Mussoorie, says of this one: "Like R. affinis , this species may frequently be heard during its flight cracking and crunching the hard wings of beetles, which in the evening hours are usually abundant among the trees; the teeth are strong, and the tout ensemble of its aspect is not unlike that of a bull-dog."—'Proc. Zoo. Soc.,' 1872, page 701.
HABITAT.—Burmah (Moulmein).
DESCRIPTION.—This bat resembles the last closely; such difference as exists is that the concave surface of the terminal nose-leaf is divided into two cells only by a single central vertical ridge, and from the under surface of the juncture of the mandible a small bony process projects downwards about equal to the lower canine tooth in vertical extent, and covered by the integument.
There is an excellent figure of this bat in Dobson's Monograph, from whence I have also taken the above description.
HABITAT.—Nicobar Island.
DESCRIPTION.—"Ears large, acute; outer margin slightly concave beneath the tip; no frontal sac behind the nose-leaf; upper margin of the transverse terminal leaf simple, forming an arc of a circle, folded back and overhanging the concave front surface, which is divided into two cells only by a single central longitudinal ridge; in front the margin of the horse-shoe is marked by three small points" ( Dobson ). Fur light brown, then greyish, with light brown tips.
SIZE.—Length of head and body, 3 inches.
HABITAT.—The entire range of the Himalayas, Khasya Hills, and Ceylon.
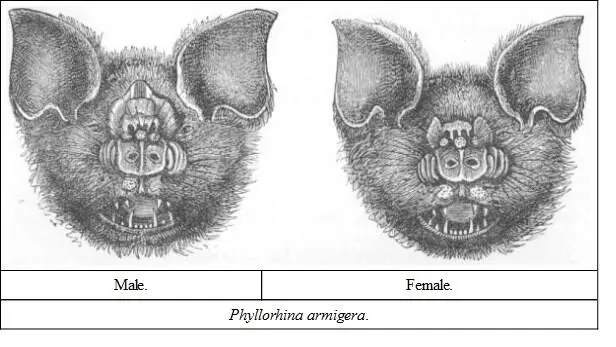
DESCRIPTION.—The hinder erect nose-leaf narrow, not so broad as the horse-shoe; upper edge sinuate, slightly elevated in the centre, and at either extremity; vertical ridges beneath well developed, prominent, enclosing moderately deep cells; wart-like granular elevations on each side above the eyes are usually greatly developed, forming large thickened longitudinal elevations extending forward on each side of the posterior erect nose-leaf, and backwards towards the frontal sac ( Dobson ). The colour varies.
SIZE.—Length of head and body from 3 to 4 inches; tail about 2.
This is the largest of this genus, and one of the most interesting of the species. My space will not admit of extensive quotations from those who have written about it, but there is a fuller description of it in Dr. Dobson's book, and a very interesting account of its habits by Capt. J. Hutton, in the 'Proceedings of the Zoological Society,' 1872, page 701.
HABITAT.—Khasya Hills.
DESCRIPTION.—Ears large, broad, triangular, with subacute tips; outer margin slightly concave; upper transverse nose-leaf small; upper edge simple, narrower than horse-shoe, thin; three vertical folds in front faintly descernible at base only; horse-shoe with small incision in centre of front free edge; frontal pore small, placed at some distance behind the transverse nose-leaf; fur and integuments dark throughout.— Dobson .
SIZE.—Length of head and body, 2 inches; tail, 1-6/10.
HABITAT.—Central India, Deccan.
DESCRIPTION.—"Ear comparatively small, as broad as long; inner margin very convex forward; outer margin slightly concave beneath the tip; nose-leaf as in P. larvata , but the transverse terminal leaf is more rectangular; the superior margin less convex, and its concave front surface is marked by three very prominent vertical ridges; frontal pore small, indistinct, not larger than in the females of P. larvata ."— Dobson .
SIZE.—Head and body about 2 inches; tail, 1 inch.
HABITAT.—India (N. W. Himalaya), Nicobar Islands.
DESCRIPTION.—Fur above reddish chestnut; the base of the hairs pale reddish-white, or base of hair pure white, the tip, dark reddish-brown. Ears as long as the head, broad; the lower half of the inner margin very convex; the summit of the ear conch rounded off broadly as far as a point on the outer side, where a slight but distinct flattening occurs, and indicates the position of the tip. Horse-shoe small, square; the concave front surface divided into four cells by three distinct vertical ridges; no secondary leaflets external to the horse-shoe; frontal sac distinct in males, rudimentary in females ( Dobson ). Blyth includes this bat in his Burmese Catalogue, but does not say much about it.
Possesses the general characteristics of Rhinolophus , but the tail and calcanea wanting entirely; the intercrural membrane acutely emarginate to the depth of a line even with the knees; ears large, broad and rounded; the summit of the facial membranes rising abruptly, obtusely bifid, bent forward; fur long, delicately fine.— Jerdon .
Dental formula: Inc., 1—1/4; can., 1—1/1—1; premolars, 2—2/2—2; molars, 3—3/3—3.
HABITAT.—The Sunderbunds, Bengal.
DESCRIPTION.—Colour dusky or blackish; the fur tipped with ashy brown above, paler and somewhat ashy beneath; membranes fuscous.
SIZE.—Length, 1-7/8 inch; membrane beyond ¾ inch; forearm, 1¾.
This bat is rare. The above description, given by Jerdon, is based on one specimen sent to Mr. Blyth by Mr. Frith, who obtained it in the Sunderbunds. It also inhabits Java. Dr. Dobson examined a specimen from thence in the Leyden Museum. He says: "Calcanea and tail very short," whereas the above description says entirely wanting. "The ears are funnel-shaped, and thickly covered with fine hair. Metacarpal bone of thumb very long; the wing membrane enclosing the thumb up to the base of the claw; wing to the tarsus close to the ankles; feet very slender; toes with strong claws."
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Natural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












