Ernest Seton - Wild Animals at Home
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Ernest Seton - Wild Animals at Home» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Год выпуска: 2009, Жанр: Природа и животные, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Wild Animals at Home
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:2009
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:5 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 100
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Wild Animals at Home: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Wild Animals at Home»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Wild Animals at Home — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Wild Animals at Home», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
A NARROW-GAUGE MULE—THE PRAIRIE HARE

One has to see this creature with its great flopping ears, and its stiff-legged jumping like a bucking mule, to realize the aptness of its Western nickname.
As it bounds away from your pathway its bushy snow-white tail and the white behind the black-tipped ears will point out plainly that it is neither the Texas Jackrabbit nor the Rocky Mountain Cottontail, but the White-tailed Jackrabbit, the finest of all our Hares.
I have met it in woods, mountains, and prairies, from California to Manitoba and found it the wildest of its race and almost impossible of approach; except in the great exceptional spot, the Yellowstone Park. Here in the August of 1912 I met with two, close to the Mammoth Hot Springs Hotel. At a distance of thirty feet they gave me good chances to take pictures, and though the light was very bad I made a couple of snaps. Fifteen years ago, when first I roamed in the Park, the Prairie Hare was exceedingly rare, but now, like so many of the wild folk, it has become quite common. Another evidence of the efficacy of protection.
This silvery-gray creature turns pure white in the winter, when the snow mantle of his range might otherwise make it too conspicuous.
THE BUMP OF MOSS THAT SQUEAKS
No matter how horrible a certain climate or surroundings may seem to us, they are sure to be the ideal of some wild creature, its very dream of bliss. I suppose that slide rock, away up in cold, bleak, windy country above the timber-line, is absolutely the unloveliest landscape and most repulsive home ground that a man could find in the mountains and yet it is the paradise, the perfect place of a wonderful little creature that is found on the high peaks of the Rockies from California to Alaska.
It is not especially abundant in the Yellowstone Park, but it was there that first I made its acquaintance, and Easterners will meet with it in the great Reserve more often than in all other parts of its range put together.

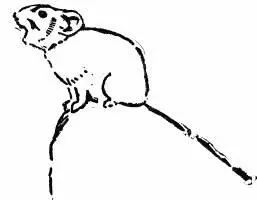
As one reaches the Golden Gate, near Mammoth Hot Springs, many little animals of the Ground-squirrel group are seen running about, and from the distance comes a peculiar cry, a short squeak uttered every ten or fifteen seconds. You stop, perhaps search with your eye the remote hillside, but you are looking too far afield. Glance toward the tumbled rock piles, look at every high point. There on top of one you note a little gray lump, like a bump of moss, the size of your fist, clinging to the point of the rock. Fix your glasses on it, and you will see plainly that the squeak is made by this tiny creature, like a quarter-grown Rabbit with short, round, white-rimmed ears and no visible tail. This is the curious little animal that cannot be happy anywhere but in the slide rock; this is the Calling Hare. "Little Chief Hare" is its Indian name, but it has many others of much currency, such as "Pika," and "Starved Rat," the latter because it is never fat. The driver calls it a "Coney," or "Rock Rabbit." In its colour, size, shape, and habits it differs from all other creatures in the region; it is impossible to mistake it. Though a distant kinsman of the Rabbits, it is unlike them in looks and ways. Thus it has, as noted, the very un-rabbit-like habit of squeaking from some high lookout. This is doubtless a call of alarm to let the rest of the company know that there is danger about, for the Coney is a gregarious creature; there may be a hundred of them in the rock-slide.
Some years ago, in Colorado, I sketched one of the Coneys by help of a field glass. He was putting all the force of his energetic little soul into the utterance of an alarm cry for the benefit of his people.
But the most interesting habit of this un-rabbity Rabbit is its way of preparing for winter.

When the grass, the mountain dandelions, and the peavines are at their best growth for making hay, the Coney, with his kind, goes warily from his stronghold in the rocks to the nearest stretch of herbage, and there cuts as much as he can carry of the richest growths; then laden with a bundle as big as himself, and very much longer, he makes for the rocks, and on some flat open place spreads the herbage out to be cured for his winter hay. Out in full blaze of the sun he leave it, and if some inconsiderate rock comes in between, to cast a shadow on his hay a-curing, he moves the one that is easiest to move; he never neglects his hay. When dry enough to be safe, he packs it away into his barn, the barn being a sheltered crevice in the rocks where the weather cannot harm it, and where it will continue good until the winter time, when otherwise there would be a sad pinch of famine in the Coney world. The trappers say that they can tell whether the winter will be hard or open by the amount of food stored up in the Coney barns.
Many a one of these I have examined in the mountains of British Columbia and Colorado, as well as in the Park. The quantity of hay in them varies from what might fill a peck measure to what would make a huge armful. Among the food plants used, I found many species of grass, thistle, meadow-rue, peavine, heath, and the leaves of several composite plants. I suspect that fuller observations will show that they use every herb not actually poisonous, that grows in the vicinity of their citadel. More than one of these wads of hay had in the middle of it a nest or hollow; not, I suspect, the home nest where the young are raised, but a sort of winter restaurant where they could go while the ground was covered with snow, and sitting in the midst of their provisions, eat to their heart's content.
It is not unlikely that in this we see the growth of the storage habit, beginning first with a warm nest of hay, which it was found could be utilized for food when none other was available. The fact that these barns are used year after year is shown by the abundance of pellets in several layers which were found in and about them.
THE WEATHERWISE CONEY
A very wise little people is this little people of the Rocks. Not only do they realize that in summer they must prepare for winter, but they know how to face a present crisis, however unexpected. To appreciate the following instance, we must remember that the central thought in the Coney's life is his "grub pile" for winter use, and next that he is a strictly daytime animal. I have often slept near a Coney settlement and never heard a sound or seen a sign of their being about after dark. Nevertheless, Merriam tells us that he and Vernon Bailey once carried their blankets up to a Coney colony above timber-line in the Salmon River Mountains of Idaho, intending to spend the night there and to study the Coneys whose piles of hay were visible in all directions on their rocks. As this was about the first of September, it was natural to expect fair weather and a complete curing of the hay in a week or so. But a fierce storm set in with the descending night. The rain changed to hail and then to snow, and much to the surprise of the naturalists, they heard the squeak of the Coneys all night long.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Wild Animals at Home»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Wild Animals at Home» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Wild Animals at Home» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.





