So, JIT became Lean when it was recognised that parts arriving only when required and only in the quantities required is only a part of the story.
Source: www.training-management.info, Ian Henderson
1. Material Requirements Planning– планирование потребности в материалах
2. Manufacturing Resource Planning– планирование производственных ресурсов
3. stock n – акция; товарные запасы
4. sophistication n – искушенность, изощренность, сложность
sophisticated a – искушенный, изощренный, сложный
5. lead time– время между размещением заказа и получением материалов от поставщика; время между началом производственного процесса и изготовлением первого изделия или всей партии
6. inventory n – запасы
7. just-in-time (JIT)– система «точно в срок»
8. breakthrough n – прорыв
9. highlight n – центр внимания, основной момент
highlight v – освещать, выдвигать на первый план
10. counterpart n – двойник, аналог, копия, дубликат; противная сторона
11. batch n – партия, группа
12. order n – приказ, распоряжение; заказ
order v – приказывать, распоряжаться; заказывать
13. set-up n – установка, наладка, система
set up v – устанавливать, налаживать
14. offset n – зачет, компенсация, возмещение
offset v – зачитывать, компенсировать, возмещать
15. workload n – рабочая нагрузка
16. Master Production Scheduling– главный план-график производства
17. accounting n – бухгалтерский учет
accounting a – бухгалтерский
18. accounting conventions– учетные правила
19. compliance n – согласие, соответствие правилам, соблюдение (законов, правил)
comply (with) v – соглашаться, соответствовать, соблюдать
20. quality circles– кружки качества
21. demand n – спрос, требование, потребность, нужда
demand v – требовать
demanding a – требовательный, сложный
22. failure n – неудача, провал, банкротство; отказ (в работе), повреждение, срыв, авария
fail v – потерпеть неудачу, провалиться, обанкротиться; отказать
23. expediting n – связь с поставщиками, время исполнения (время для розыска и выполнения потерянного или неправильно направленного заказа)
expeditor n – диспетчер, экспедитор
expedite v – ускорять
24. work-in-progress (WIP)– незавершенное производство, полуфабрикаты
25. cycle time– время рабочего цикла
26. layout n – схема расположения, компоновка, планировка, чертеж
lay out v – располагать, размещать; выделять средства
27. waste n – отходы, потери; расточительство, перерасход
waste v – терять, тратить попусту, расточать
28. dedication n – посвящение, преданность, приверженность
dedicate v – посвящать
dedicated a – посвященный, приверженный, преданный
29. lean manufacturing– рациональное производство
Exercise 1. Answer the following questions.
1. What were the news from Japan that amazed the US manufactureres and scholars around 1980? 2. What was the company that pioneered the development of the Japanese manufacturing principles? 3. Why did the US companies manufacture components and parts in large batches? 4. Why did the US companies hold safety stocks? 5. What were the ideas of the US quality gurus that the Japanese successfully applied? 6. What other contributors to improved quality did the JIT approach consider? 7. What was the underlying principle of the quality circles? 8. Why were partnership relations with suppliers so important? 9. Why does it make economic sense to eliminate variety? 10. How did the Japanese shorten cycle times? 11. What was the basic idea of kanban? 12. Why were the Japanese companies happy when they discovered some problem in a process? 13. What is the key premise of the Lean Manufacturing?
Exercise 2. An American car manufacturer hired a Japanese consultant to help enhance its competitiveness and cut costs. The advisor suggested applying some of the Japanese manufacturing principles. Invent a dialogue between the US vice-president for production and the foreign consultant. Use the following terms.
JIT
kanban
batch size
safety stocks
long-term partnership relations with suppliers
elimination of variety
shorter cycle-times
quality circles
elimination of waste
problem-solving
lean manufacturing
commitment to excellence
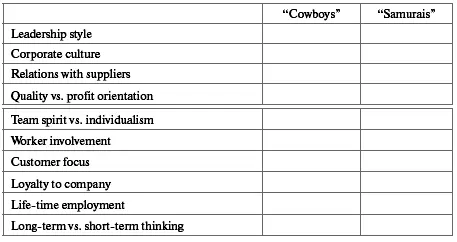
Exercise 3. Compare the American and Japanese management principles along the following lines.
Exercise 4*. Fill in the blanks using terms given below.
The Characteristics of the Japanese Approach to Business
The system of…….. in the large organizations is called Nenko Seido . This means:
– guaranteed employment until……… at 55;
– promotion and……….. by seniority;
– an internal labor market meaning………. from within the company;
– extensive…….. with an emphasis on long-term behavior, attitudes and performance;
– extensive……… package, which is regarded as a right and incorporates the needs of the workers’ family;
Читать дальше
Конец ознакомительного отрывка
Купить книгу





![Владимир Аракин - Практический курс английского языка 3 курс [calibre 2.43.0]](/books/402486/vladimir-arakin-prakticheskij-kurs-anglijskogo-yazyk-thumb.webp)







