Christopher Ryan - Sex at Dawn
Здесь есть возможность читать онлайн «Christopher Ryan - Sex at Dawn» весь текст электронной книги совершенно бесплатно (целиком полную версию без сокращений). В некоторых случаях можно слушать аудио, скачать через торрент в формате fb2 и присутствует краткое содержание. Жанр: Прочая научная литература, на английском языке. Описание произведения, (предисловие) а так же отзывы посетителей доступны на портале библиотеки ЛибКат.
- Название:Sex at Dawn
- Автор:
- Жанр:
- Год:неизвестен
- ISBN:нет данных
- Рейтинг книги:4 / 5. Голосов: 1
-
Избранное:Добавить в избранное
- Отзывы:
-
Ваша оценка:
- 80
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Sex at Dawn: краткое содержание, описание и аннотация
Предлагаем к чтению аннотацию, описание, краткое содержание или предисловие (зависит от того, что написал сам автор книги «Sex at Dawn»). Если вы не нашли необходимую информацию о книге — напишите в комментариях, мы постараемся отыскать её.
Sex at Dawn — читать онлайн бесплатно полную книгу (весь текст) целиком
Ниже представлен текст книги, разбитый по страницам. Система сохранения места последней прочитанной страницы, позволяет с удобством читать онлайн бесплатно книгу «Sex at Dawn», без необходимости каждый раз заново искать на чём Вы остановились. Поставьте закладку, и сможете в любой момент перейти на страницу, на которой закончили чтение.
Интервал:
Закладка:
Once people were farming the same land season after season, private property quickly replaced communal ownership as the modus operandi in most societies. For nomadic foragers, personal property—anything needing to be carried—is kept to a minimum, for obvious reasons. There is little thought given to who owns the land, or the fish in the river, or the clouds in the sky. Men (and often, women) confront danger together. An individual male’s parental investment, in other words—the core element of the standard narrative—tends to be diffuse in societies like those in which we evolved, not directed toward one particular woman and her children, as the conventional model insists.
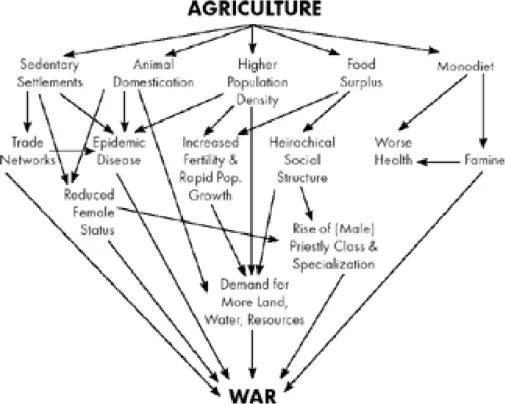
But when people began living in settled agricultural communities, social reality shifted deeply and irrevocably. Suddenly it became crucially important to know where your field ended and your neighbor’s began. Remember the Tenth Commandment: “Thou shalt not covet thy neighbour’s house, thou shalt not covet thy neighbour’s wife, nor his manservant, nor his maidservant, nor his ox, nor his ass, nor any thing that [is] thy neighbour’s.” Clearly, the biggest loser (aside from slaves, perhaps) in the agricultural revolution was the human female, who went from occupying a central, respected role in foraging societies to becoming another possession for a man to earn and defend, along with his house, slaves, and livestock.
“The origins of farming,” says archaeologist Steven Mithen, “is the defining event of human history—the one turning point that has resulted in modern humans having a quite different type of lifestyle and cognition to all other animals and past types of humans.” 10The most important pivot point in the story of our species, the shift to agriculture redirected the trajectory of human life more fundamentally than the control of fire, the Magna Carta, the printing press, the steam engine, nuclear fission, or anything else has or, perhaps, ever will. With agriculture, virtually everything changed: the nature of status and power, social and family structures, how humans interacted with the natural world, the gods they worshipped, the likelihood and nature of warfare between groups, quality of life, longevity, and certainly, the rules governing sexuality. His survey of the relevant archaeological evidence led archaeologist Timothy Taylor, author of The Prehistory of Sex, to state, “While hunter-gatherer sex had been modeled on an idea of sharing and complementarity, early agriculturalist sex was voyeuristic, repressive, homophobic, and focused on reproduction.” “Afraid of the wild,” he concludes, “farmers set out to destroy it.” 11
Land could now be possessed, owned, and passed down the generations. Food that had been hunted and gathered now had to be sowed, tended, harvested, stored, defended, bought, and sold. Fences, walls, and irrigation systems had to be built and reinforced; armies to defend it all had to be raised, fed, and controlled. Because of private property, for the first time in the history of our species, paternity became a crucial concern.
But the standard narrative insists that paternity certainty has always been of utmost importance to our species, that our very genes dictate we organize our sexual lives around it. Why, then, is the anthropological record so rich with examples of societies where biological paternity is of little or no importance? Where paternity is unimportant, men tend to be relatively unconcerned about women’s sexual fidelity.
But before we get into these real-life examples, let’s take a quick trip to the Yucatan.
*
We use the terms “foragers” and “hunter-gatherers” interchangeably throughout the text.
*
Anthropologist James Woodburn (1981/1998) classified foraging societies into immediate-return (simple) and delayed-return (complex) systems. In the former, food is eaten within days of acquisition, without elaborate processing or storage. Unless otherwise noted, we refer to these societies.
P A R T I
On the Origin of the Specious
CHAPTER ONE Remember the Yucatan!
The function of the imagination is not to make strange things settled, so much as to make settled things strange.
G. K. CHESTERTON
Forget the Alamo. The Yucatan provides a more useful lesson.
It was early spring, 1519. Hernan Cortes and his men had just arrived off the coast of the Mexican mainland. The conquistador ordered his men to bring one of the natives to the deck of the ship, where Cortes asked him the name of this exotic place they’d found. The man responded, “Ma c’ubah than,” which the Spanish heard as Yucatan. Close enough. Cortes proclaimed that from that day onward, Yucatan and any gold it contained belonged to the king and queen of Spain, and so on.
Four and a half centuries later, in the 1970s, linguists researching archaic Mayan dialects concluded that Ma c’ubah than meant “I do not understand you.” 1
Each spring, thousands of American university students celebrate with wet T-shirt contests, foam parties, and Jell-O wrestling on the beautiful beaches of the I Do Not Understand You Peninsula.
But confusion mistaken for knowledge isn’t limited to spring break. We all fall into this trap. (One night, over dinner, a close friend mentioned that her favorite Beatles song is “Hey Dude.”) Despite their years of training, even scientific types slip into thinking they are observing something when in fact they are simply projecting their biases and ignorance. What trips up the scientists is the same cognitive failing we all share: it’s hard to be certain about what we think we know, but don’t really. Having misread the map, we’re sure we know where we are. In the face of evidence to the contrary, most of us tend to go with our gut, but the gut can be an unreliable guide.
Take food, for example. We all assume that our craving or disgust is due to something about the food itself—as opposed to being an often arbitrary response preprogrammed by our culture. We understand that Australians prefer cricket to baseball, or that the French somehow find Gerard Depardieu sexy, but how hungry would you have to be before you would consider plucking a moth from the night air and popping it, frantic and dusty, into your mouth? Flap, crunch, ooze. You could wash it down with some saliva beer. How does a plate of sheep’s brain sound? Broiled puppy with gravy? May we interest you in pig’s ears or shrimp heads? Perhaps a deep-fried songbird that you chew up, bones, beak, and all? A game of cricket on a field of grass is one thing, but pan-fried crickets over lemongrass? That’s revolting.
Or is it? If lamb chops are fine, what makes lamb brains horrible? A pig’s shoulder, haunch, and belly are damn fine eatin’, but the ears, snout, and feet are gross? How is lobster so different from grasshopper? Who distinguishes delectable from disgusting, and what’s their rationale? And what about all the exceptions? Grind up those leftover pig parts, stuff ‘em in an intestine, and you’ve got yourself respectable sausages or hot dogs. You may think bacon and eggs just go together, like French fries and ketchup or salt and pepper. But the combination of bacon and eggs for breakfast was dreamed up about a hundred years ago by an advertising agency hired to sell more bacon, and the Dutch eat their fries with mayonnaise, not ketchup.
Think it’s rational to be grossed out by eating bugs? Think again. A hundred grams of dehydrated cricket contains 1,550 milligrams of iron, 340 milligrams of calcium, and 25 milligrams of zinc—three minerals often missing in the diets of the chronic poor. Insects are richer in minerals and healthy fats than beef or pork. Freaked out by the exoskeleton, antennae, and way too many legs? Then stick to the Turf and forget the Surf because shrimp, crabs, and lobsters are all arthropods, just like grasshoppers. And they eat the nastiest of what sinks to the bottom of the ocean, so don’t talk about bugs’ disgusting diets. Anyway, you may have bug parts stuck between your teeth right now. The Food and Drug Administration tells its inspectors to ignore insect parts in black pepper unless they find more than 475 of them per 50 grams, on average. 2A fact sheet from the University of Ohio estimates that Americans unknowingly eat an average of between one and two pounds of insects per year.
Читать дальшеИнтервал:
Закладка:
Похожие книги на «Sex at Dawn»
Представляем Вашему вниманию похожие книги на «Sex at Dawn» списком для выбора. Мы отобрали схожую по названию и смыслу литературу в надежде предоставить читателям больше вариантов отыскать новые, интересные, ещё непрочитанные произведения.
Обсуждение, отзывы о книге «Sex at Dawn» и просто собственные мнения читателей. Оставьте ваши комментарии, напишите, что Вы думаете о произведении, его смысле или главных героях. Укажите что конкретно понравилось, а что нет, и почему Вы так считаете.












