After another 400 million years, gas nebulae arise. Thanks to the force of gravitational attraction, the gas concentrates in the stars and, with billions of luminaries, galaxies.
Our Galaxy (with a capital letter), otherwise – the Milky Way (Latin – via lactea) is formed 13 billion years ago, and has 200 to 400 billion stars. The age of the Solar System is 4.5 billion years. It has 8 recognized classical planets, as well as 5 so-called dwarf ones, including now also “expelled” from group “A” Pluto.
Our Earth, according to a widespread theory, originated from a protoplanetary disk, around this time. Strangely enough, the first, primitive forms of life, nuclear-free cells, prokaryotes, appeared almost almost immediately after the termination of the devastating asteroid bombardment (the eon of Qatarhei, 600 million years), as well as education, as a result of a terrible sliding strike on our planet, an object the size of Mars, the future companion of all lovers, the Moon. However, for another long and a half billion years, the stage of development, called Archean, life forms do not develop much. The top of this demiurgic process is unicellular eukaryotes and already relatively complex algae visible to the naked eye.
All these organisms, presumably, have a single, universal common ancestor. The genetic set of all living things on Earth is the same. Their DNA is assembled from four nucleotides (biological molecules) – adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine.
Рroterozoic – (other Greek approximately as “earlier life”) – the longest geological period, 2 billion years, starts a little more than 2.5 billion years ago. For one reason or another, oxygen accumulates in the atmosphere – and it leads to the extinction of almost all anaerobic creatures. The ozone layer is formed. The next trouble for the already accustomed organisms to new conditions is the great Huronian glaciation (2.4—2.1 billion years ago). Methane combines with oxygen, forms carbon dioxide (which contributes much less to the greenhouse effect), as a result – the Earth turns into a huge “snowball”. At the equator, it is almost as cold as in modern Antarctica. Life is preserved in relatively small polynyas and ponds with melt water.
Volcanoes gradually increase the level of carbon dioxide and methane. A new perturbation is being prepared. For a thousand years, significant areas are freed of ice, and the planet’s climate, on the whole, returns to the norm known to us.
The second option, explaining the presence of signs of ancient glaciers in the equatorial regions of the planet – a fairly rapid turn of the poles of the Earth, followed (300 million years) by their return to the site.
Somehow, sea sponges appear, that is, aquatic multicellular animals that lead an attached lifestyle, as well as mushrooms, essence, eukaryotic communities that combine the signs of plants and animals. As a result of their vital activity, soil appears.
The single continent of Rodinia splits into two parts, which diverge to the poles. The northern half is Laurasia, the southern half is Gondwana.
The sun, meanwhile, increases luminosity by 12%. The Age of Precambrian or Cryptozoic, the “Hidden Life”, (sometimes called the eons of Archean and the Proterozoic together) ends.
Multicellular creatures, animals, higher plants, are 580 million years ago, thus assuming the onset of the turbulent Phanerozoic (“clear life”) eon – in which we live, too. His first era – Paleozoic (“ancient life”). It is divided into six periods: Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. They last for 20 to 60 million years.
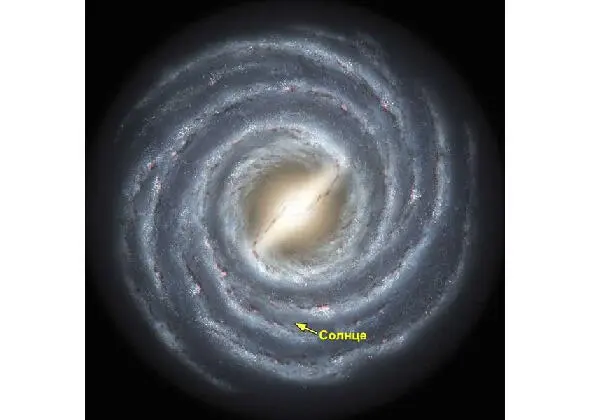

Galaxy the Milky Way. Reconstruction
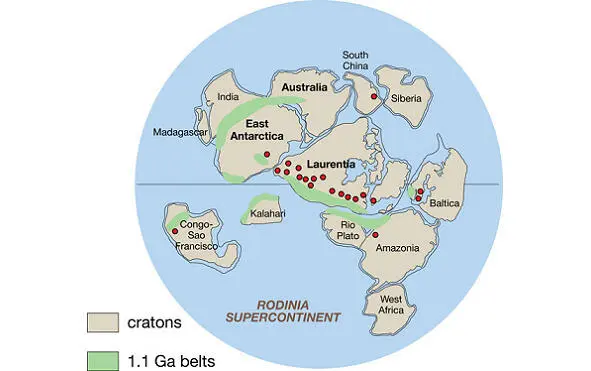
continent of Rodinia
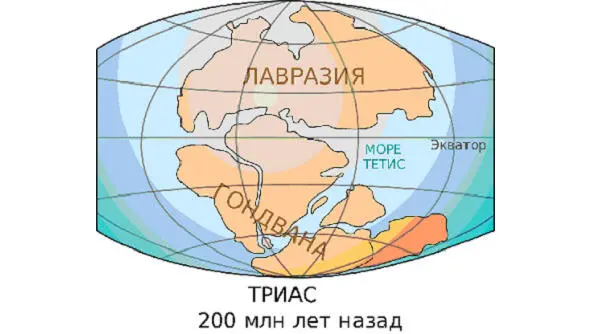
Laurasia and Gondwana

Trilobite

Ammonite
Stegotsefal

Meganevra (reconstruction)

Shellfish
Seismosaurus
Ankylosaurus, recognized symbol of the Mesozoic era

Pteranodone

Representative of the order Mesonihia, the ancestor of whales, according to the theory of Darwin
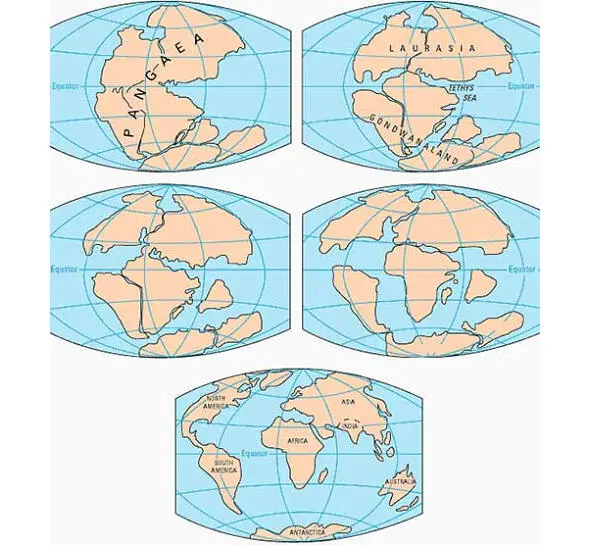
Evolution of the continents; from Laurasia, Gondwana and Pangea to the modern form

Mastodon

The Modern Earth. A photo from the Apollo-17, 1 hour 54 minutes after reaching the flight path to the Moon (1972)
In the Cambrian organisms, first of all, learn to build strong skeletons, according to which they are detected by paleontologists. The star of this period is trilobite, a pretty pretty arthropod, a prototype of modern cancer. There are also those that, with some stretch, can be classified as cephalopods – reminiscent of octopuses and squid. Their flowering falls on the Ordovician. The Silurian, which lasts “only” 25 million years, is marked by two mass extinctions (up to 50% of the marine life). One of them, which occurred 443 million years ago, the so-called. Ordovician-Silurian is probably due to the movement of Gondwana to the South Pole, as well as a sharp drop in the ocean level. Especially got, already was prosperous brachiopods (something like oysters), bivalve molluscs, bryozoans (colonies of small worms) and corals. The Devonian period is characterized by terrestrial vertebrates, famous brush-trotter fish, insects, as well as gymnosperms (“bare” seeds hide in cones), fern-like and horsetail. Racoscorpions and fish appear. Trilobites, on the contrary, with such an abundance of predators, are rapidly dying out. However, the massive sea at the end of the Devonian, affects more than half of the entire marine life and flora; the reason for this, perhaps – the notorious comet.
Читать дальше



























