Due to the work of Einstein, physicists realized that by demanding that the speed of light be the same in all frames of reference, Maxwell’s theory of electricity and magnetism dictates that time cannot be treated as separate from the three dimensions of space. Instead, time and space are intertwined. It is something like adding a fourth direction of future/past to the usual left/right, forward/backward, and up/down. Physicists call this marriage of space and time “space-time,” and because space-time includes a fourth direction, they call it the fourth dimension. In space-time, time is no longer separate from the three dimensions of space, and, loosely speaking, just as the definition of left/right, forward/backward, or up/down depends on the orientation of the observer, so too does the direction of time vary depending on the speed of the observer. Observers moving at different speeds would choose different directions for time in space-time. Einstein’s theory of special relativity was therefore a new model, which got rid of the concepts of absolute time and absolute rest (i.e., rest with respect to the fixed ether).
Einstein soon realized that to make gravity compatible with relativity another change was necessary. According to Newton’s theory of gravity, at any given time objects are attracted to each other by a force that depends on the distance between them at that time. But the theory of relativity had abolished the concept of absolute time, so there was no way to define when the distance between the masses should be measured. Thus Newton’s theory of gravity was not consistent with special relativity and had to be modified. The conflict might sound like a mere technical difficulty, perhaps even a detail that could somehow be worked around without much change in the theory. As it turned out, nothing could have been further from the truth.
Over the next eleven years Einstein developed a new theory of gravity, which he called general relativity. The concept of gravity in general relativity is nothing like Newton’s. Instead, it is based on the revolutionary proposal that space-time is not flat, as had been assumed previously, but is curved and distorted by the mass and energy in it.
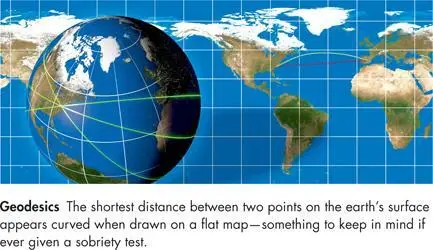
A good way to picture curvature is to think of the surface of the earth. Although the earth’s surface is only two-dimensional (because there are only two directions along it, say north/south and east/west), we’re going to use it as our example because a curved two-dimensional space is easier to picture than a curved four-dimensional space. The geometry of curved spaces such as the earth’s surface is not the Euclidean geometry we are familiar with. For example, on the earth’s surface, the shortest distance between two points-which we know as a line in Euclidean geometry-is the path connecting the two points along what is called a great circle. (A great circle is a circle along the earth’s surface whose center coincides with the center of the earth. The equator is an example of a great circle, and so is any circle obtained by rotating the equator along different diameters.)
Imagine, say, that you wanted to travel from New York to Madrid, two cities that are at almost the same latitude. If the earth were flat, the shortest route would be to head straight east. If you did that, you would arrive in Madrid after traveling 3,707 miles. But due to the earth’s curvature, there is a path that on a flat map looks curved and hence longer, but which is actually shorter. You can get there in 3,605 miles if you follow the great-circle route, which is to first head northeast, then gradually turn east, and then southeast. The difference in distance between the two routes is due to the earth’s curvature, and a sign of its non-Euclidean geometry. Airlines know this, and arrange for their pilots to follow great-circle routes whenever practical.
According to Newton’s laws of motion, objects such as cannonballs, croissants, and planets move in straight lines unless acted upon by a force, such as gravity. But gravity, in Einstein’s theory, is not a force like other forces; rather, it is a consequence of the fact that mass distorts space-time, creating curvature. In Einstein’s theory, objects move on geodesics, which are the nearest things to straight lines in a curved space. Lines are geodesics on the flat plane, and great circles are geodesics on the surface of the earth. In the absence of matter, the geodesics in four-dimensional space-time correspond to lines in three-dimensional space. But when matter is present, distorting space-time, the paths of bodies in the corresponding three-dimensional space curve in a manner that in Newtonian theory was explained by the attraction of gravity. When space-time is not flat, objects’ paths appear to be bent, giving the impression that a force is acting on them.
Einstein’s general theory of relativity reproduces special relativity when gravity is absent, and it makes almost the same predictions as Newton’s theory of gravity in the weak-gravity environment of our solar system-but not quite. In fact, if general relativity were not taken into account in GPS satellite navigation systems, errors in global positions would accumulate at a rate of about ten kilometers each day! However, the real importance of general relativity is not its application in devices that guide you to new restaurants, but rather that it is a very different model of the universe, which predicts new effects such as gravitational waves and black holes. And so general relativity has transformed physics into geometry. Modern technology is sensitive enough to allow us to perform many sensitive tests of general relativity, and it has passed every one.
Though they both revolutionized physics, Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism and Einstein’s theory of gravity-general relativity-are both, like Newton’s own physics, classical theories. That is, they are models in which the universe has a single history. As we saw in the last chapter, at the atomic and subatomic levels these models do not agree with observations. Instead, we have to use quantum theories in which the universe can have any possible history, each with its own intensity or probability amplitude. For practical calculations involving the everyday world, we can continue to use classical theories, but if we wish to understand the behavior of atoms and molecules, we need a quantum version of Maxwell’s theory of electromagnetism; and if we want to understand the early universe, when all the matter and energy in the universe were squeezed into a small volume, we must have a quantum version of the theory of general relativity. We also need such theories because if we are seeking a fundamental understanding of nature, it would not be consistent if some of the laws were quantum while others were classical. We therefore have to find quantum versions of all the laws of nature. Such theories are called quantum field theories.
The known forces of nature can be divided into four classes:
1. Gravity. This is the weakest of the four, but it is a long-range force and acts on everything in the universe as an attraction. This means that for large bodies the gravitational forces all add up and can dominate over all other forces.
2. Electromagnetism. This is also long-range and is much stronger than gravity, but it acts only on particles with an electric charge, being repulsive between charges of the same sign and attractive between charges of the opposite sign. This means the electric forces between large bodies cancel each other out, but on the scales of atoms and molecules they dominate. Electromagnetic forces are responsible for all of chemistry and biology.
3. Weak nuclear force. This causes radioactivity and plays a vital role in the formation of the elements in stars and the early universe. We don’t, however, come into contact with this force in our everyday lives.
Читать дальше