(ii) THE CIRTH
The Certhas Daeron was originally devised to represent the sounds of Sindarin only. The oldest cirth were Nos. 1, 2, 5, 6; 8, 9, 12; 18, 19, 22; 29, 31; 35, 36; 39, 42, 46, 50; and a certh varying between 13 and 15. The assignment of values was unsystematic. Nos. 39, 42, 46, 50 were vowels and remained so in all later developments. Nos. 13, 15 were used for h or s, according as 35 was used for s or h. This tendency to hesitate in the assignment of values for s and h continued in later arrangements. In those characters that consisted of a ‘stem’ and a ‘branch’, 1-31, the attachment of the branch was, if on one side only, usually made on the right side. The reverse was not infrequent, but had no phonetic significance.
The extension and elaboration of this certhas was called in its older form the Angerthas Daeron, since the additions to the old cirth and their reorganization was attributed to Daeron. The principal additions, however, the introductions of two new series, 13–17, and 23–28, were actually most probably inventions of the Noldor of Eregion, since they were used for the representation of sounds not found in Sindarin.
THE ANGERTHAS
In the rearrangement of the Angerthas the following principles are observable (evidently inspired by the Fëanorian system): (1) adding a stroke to a branch added ‘voice’; (2) reversing the certh indicated opening to a ‘spirant’; (3) placing the branch on both sides of the stem added voice and nasality. These principles were regularly carried out, except in one point. For (archaic) Sindarin a sign for a spirant m (or nasal v) was required, and since this could best be provided by a reversal of the sign for m, the reversible No. 6 was given the value m, but No. 5 was given the value hw.
No. 36, the theoretic value of which was z, was used, in spelling Sindarin or Quenya, for ss: cf. Fëanorian 31. No. 39 was used for either i or y (consonant); 34, 35 were used indifferently for s; and 38 was used for the frequent sequence nd, though it was not clearly related in shape to the dentals.

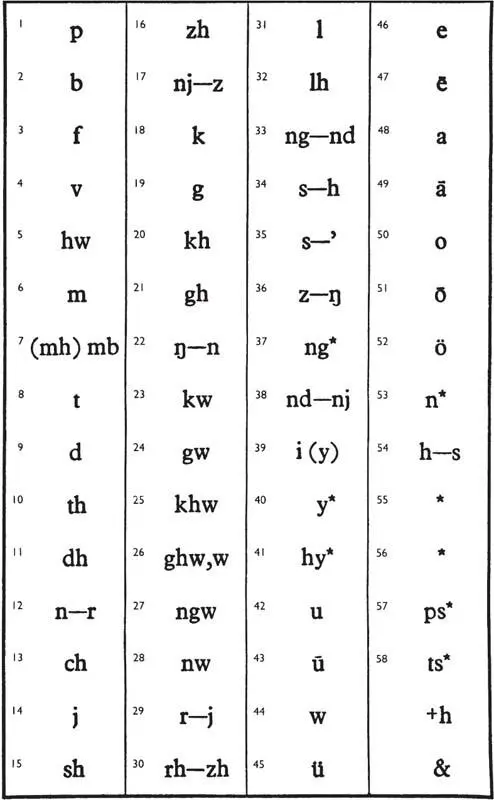
In the Table of Values those on the left are, when separated by-, the values of the older Angerthas. Those on the right are the values of the Dwarvish Angerthas Moria. [93]The Dwarves of Moria, as can be seen, introduced a number of unsystematic changes in value, as well as certain new cirth: 37, 40, 41, 53, 55, 56. The dislocation in values was due mainly to two causes: (1) the alteration in the values of 34, 35, 54 respectively to h, ’ (the clear or glottal beginning of a word with an initial vowel that appeared in Khuzdul), and s; (2) the abandonment of the Nos. 14, 16 for which the Dwarves substituted 29, 30. The consequent use of 12 for r , the invention of 53 for n (and its confusion with 22); the use of 17 as z, to go with 54 in its value s, and the consequent use of 36 as q and the new certh 37 for ng may also be observed. The new 55, 56 were in origin a halved form of 46, and were used for vowels like those heard in English butter, which were frequent in Dwarvish and in the Westron. When weak or evanescent they were often reduced to a mere stroke without a stem. This Angerthas Moria is represented in the tomb-inscription.
The Dwarves of Erebor used a further modification of this system, known as the mode of Erebor, and exemplified in the Book of Mazarbul. Its chief characteristics were: the use of 43 as z; of 17 as ks (x); and the invention of two new cirth, 57, 58 for ps and ts. They also reintroduced 14, 16 for the values j, zh; but used 29, 30 for g, gh, or as mere variants of 19, 21. These peculiarities are not included in the table, except for the special Ereborian cirth, 57, 58.
I THE LANGUAGES AND PEOPLES OF THE THIRD AGE
The language represented in this history by English was the Westron or ‘Common Speech’ of the West-lands of Middle-earth in the Third Age. In the course of that age it had become the native language of nearly all the speaking-peoples (save the Elves) who dwelt within the bounds of the old kingdoms of Arnor and Gondor; that is along all the coasts from Umbar northward to the Bay of Forochel, and inland as far as the Misty Mountains and the Ephel Dúath. It had also spread north up the Anduin, occupying the lands west of the River and east of the mountains as far as the Gladden Fields.
At the time of the War of the Ring at the end of the age these were still its bounds as a native tongue, though large parts of Eriador were now deserted, and few Men dwelt on the shores of the Anduin between the Gladden and Rauros.
A few of the ancient Wild Men still lurked in the Drúadan Forest in Anórien; and in the hills of Dunland a remnant lingered of an old people, the former inhabitants of much of Gondor. These clung to their own languages; while in the plains of Rohan there dwelt now a Northern people, the Rohirrim, who had come into that land some five hundred years earlier. But the Westron was used as a second language of intercourse by all those who still retained a speech of their own, even by the Elves, not only in Arnor and Gondor but throughout the vales of Anduin, and eastward to the further eaves of Mirkwood. Even among the Wild Men and the Dunlendings who shunned other folk there were some that could speak it, though brokenly.
OF THE ELVES
The Elves far back in the Elder Days became divided into two main branches: the West-elves (the Eldar ) and the East-elves. Of the latter kind were most of the Elven-folk of Mirkwood and Lórien; but their languages do not appear in this history, in which all the Elvish names and words are of Eldarin form. [94]Of the Eldarin tongues two are found in this book: the High-elven or Quenya, and the Grey-elven or Sindarin. The High-elven was an ancient tongue of Eldamar beyond the Sea, the first to be recorded in writing. It was no longer a birth-tongue, but had become, as it were, an ‘Elvenlatin’, still used for ceremony, and for high matters of lore and song, by the High Elves, who had returned in exile to Middle-earth at the end of the First Age.
The Grey-elven was in origin akin to Quenya; for it was the language of those Eldar who, coming to the shores of Middle-earth, had not passed over the Sea but had lingered on the coasts in the country of Beleriand. There Thingol Greycloak of Doriath was their king, and in the long twilight their tongue had changed with the changefulness of mortal lands and had become far estranged from the speech of the Eldar from beyond the Sea.
The Exiles, dwelling among the more numerous Grey-elves, had adopted the Sindarin for daily use; and hence it was the tongue of all those Elves and Elf-lords that appear in this history. For these were all of Eldarin race, even where the folk that they ruled were of the lesser kindreds. Noblest of all was the Lady Galadriel of the royal house of Finarfin and sister of Finrod Felagund, King of Nargothrond. In the hearts of the Exiles the yearning for the Sea was an unquiet never to be stilled; in the hearts of the Grey-elves it slumbered, but once awakened it could not be appeased.
Читать дальше
Конец ознакомительного отрывка
Купить книгу














